These days when we think of AI, we often think of a certain controversial chatbot (ChatGPT) that everyone seems to be using in their writing and business processes.
ChatGPT and similar platforms are a type of generative AI. As the name suggests, generative AI generates content, such as images, text, music, or even video that resemble human-generated material. It involves training models to understand and replicate patterns in data, enabling them to combine elements in unique ways to create something new.
But AI, or artificial intelligence, has a broader definition. It refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines, allowing them to perform tasks that traditionally have been performed by humans.
At MCCi when we talk about AI, we mean the functionality that incorporates automation software to create Intelligent Automation (IA). IA combines artificial intelligence with business process automation technologies to perform tasks with minimal human intervention.
As you can see on the diagram below, generative AI currently plays a limited role in business process automation.
If the AI in intelligent automation isn’t generative AI, what is it? In this blog, we’ll break down the components of IA to better understand how it uses AI.
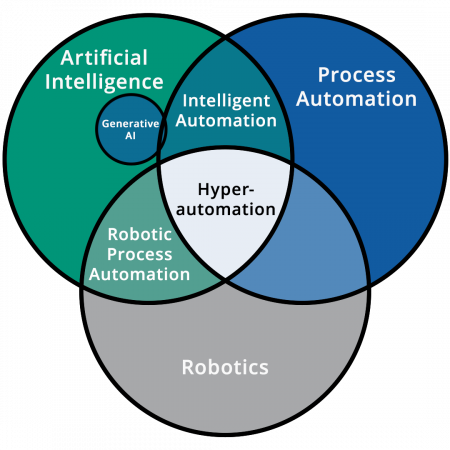
Click each term below to see its definition:
The simulation of human intelligence in machines, allowing them to perform tasks traditionally performed by humans.
Using technology, software, and tools to streamline and automate repetitive and manual tasks within an organization’s processes.
A type of AI that generates content, such as images, text, music, or even video, that resembles human-generated material.
An approach to automation that combines multiple technologies like AI, machine learning, and RPA to automate a wide range of business processes.
The combination of artificial intelligence with business process automation technologies to perform tasks with minimal human intervention.
Process automation using software “bots” that interact with multiple software applications.
What is Business Process Automation?
Business Process Automation (BPA) is the use of technology, software, and tools to streamline and automate repetitive and manual tasks within an organization’s processes. It involves identifying tasks and workflows that can be automated and implementing solutions to perform those tasks without direct human intervention.
At MCCi, most of the BPA we implement uses Laserfiche, an Enterprise Content Management platform that has the capability to automate content-related tasks using Workflows.
In Action: BPA Use Cases
This type of BPA does NOT use AI. In other words, it simply repeats the actions taken by humans without requiring the intelligence of decision-making, understanding, or analysis.
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) takes BPA a step further with the use of software “bots,” sometimes called digital workers. These bots can mimic human actions such as data entry, data extraction, and interacting with multiple software applications. RPA doesn’t require changes to the existing systems and can work with user interfaces as a human would.
One common use case for RPA is moving data between systems that don’t easily integrate with each other. Instead of a human worker manually transferring the data from one program to the other, the task is carried out by a digital worker.
In Action: RPA Use Cases
- Story, Video
Although this type of automation is growing more complex, the use cases aren’t considered “intelligent.” Again, they are simply replicating repetitive, predictable, rule-based human behaviors.
How Does Intelligent Automation Use AI?
Finally, we get to the heart of the matter. Intelligent automation combines business process automation with artificial intelligence in order to create more advanced solutions.
In essence, intelligent automation leverages AI technologies to add cognitive (“thinking”) and decision-making capabilities to automation solutions.
This combination results in systems that do more than mimic actions. They can adapt, learn, and make informed decisions, amplifying the benefits of traditional automation.
Here’s a breakdown of a few ways that intelligent automation uses AI:
Cognitive Abilities: Intelligent automation employs AI’s cognitive capabilities, such as natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and sentiment analysis, to enable systems to interact with and understand human language and unstructured data. This allows automation systems to process textual and visual information and make sense of data in context.
Learning from Data: AI technologies like machine learning enable automation systems to learn from data patterns and improve their performance over time. For instance, a technology for intelligent document processing might misidentify a Purchase Order as an Invoice Number. But if a human corrects the error, it will be more likely to identify the data correctly the next time.
Complex Decision Making: AI-equipped intelligent automation can make complex decisions by processing large volumes of data and considering various factors. These systems can weigh pros and cons, evaluate risks, and make informed choices, leading to more efficient and effective decision-making processes.
Enhanced Process Insights: By analyzing data generated during automation processes, AI can provide valuable insights into bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and optimization opportunities. This information helps organizations refine their processes and improve overall operational efficiency.
Predictive Analytics: Intelligent automation systems can use AI-based predictive analytics to forecast future outcomes based on historical data and patterns. This capability is beneficial for supply chain management, demand forecasting, financial planning, and more.
Personalization and Recommendation: AI-driven intelligent automation can personalize user experiences by analyzing user preferences and behaviors. For instance, in customer service scenarios, AI can analyze customer interactions and provide tailored recommendations or responses.
In Action: Intelligent Automation Use Case
One More Thing: Hyperautomation
Another term you’ll sometimes hear thrown around is “hyperautomation.” Hyperautomation is an approach to automation that involves multiple technologies like AI, machine learning, and RPA to automate a wide range of business processes. It goes beyond traditional automation by combining automation technologies.